1957 Ford Wiring Diagrams are essential tools for any mechanic or car enthusiast working on a classic Ford vehicle. These diagrams provide a detailed outline of the electrical system, including the wiring layout, color codes, and connections for various components.
Why are 1957 Ford Wiring Diagrams Essential?
1. Understanding the electrical system: Wiring diagrams help in understanding how the electrical system is structured and how different components are connected.
2. Troubleshooting electrical issues: By referring to the wiring diagram, it becomes easier to pinpoint the source of an electrical problem and make necessary repairs.
3. Restoring vintage vehicles: For enthusiasts restoring a 1957 Ford vehicle, the wiring diagram is crucial for ensuring the electrical system is correctly installed and functioning.
How to Read and Interpret 1957 Ford Wiring Diagrams
1. Identify components: Start by familiarizing yourself with the key components listed in the diagram, including switches, relays, and connectors.
2. Follow the wiring paths: Trace the wiring paths from one component to another, following the color codes and connection points.
3. Understand symbols: Wiring diagrams use specific symbols to represent different components, so it’s important to understand what each symbol stands for.
Using 1957 Ford Wiring Diagrams for Troubleshooting
1. Identify the problem area: Start by identifying the specific area where the electrical issue is occurring, such as a malfunctioning light or a faulty ignition system.
2. Refer to the wiring diagram: Use the diagram to trace the wiring related to the problem area and check for any loose connections, damaged wires, or faulty components.
3. Test components: Utilize a multimeter or test light to check the continuity of wires and the functionality of components as per the wiring diagram.
Importance of Safety When Working with Wiring Diagrams
1. Always disconnect the battery before working on the electrical system to prevent the risk of electric shock.
2. Use insulated tools and wear protective gear, such as gloves and safety goggles, when handling electrical components.
3. Avoid working on the electrical system in wet or damp conditions to reduce the risk of short circuits and electrical hazards.
1957 Ford Wiring Diagram
Free Auto Wiring Diagram: 1957 Ford V8 Fairlane, Custom300, or

Free Auto Wiring Diagram: 1957 Ford V8 Fairlane, Custom300, or
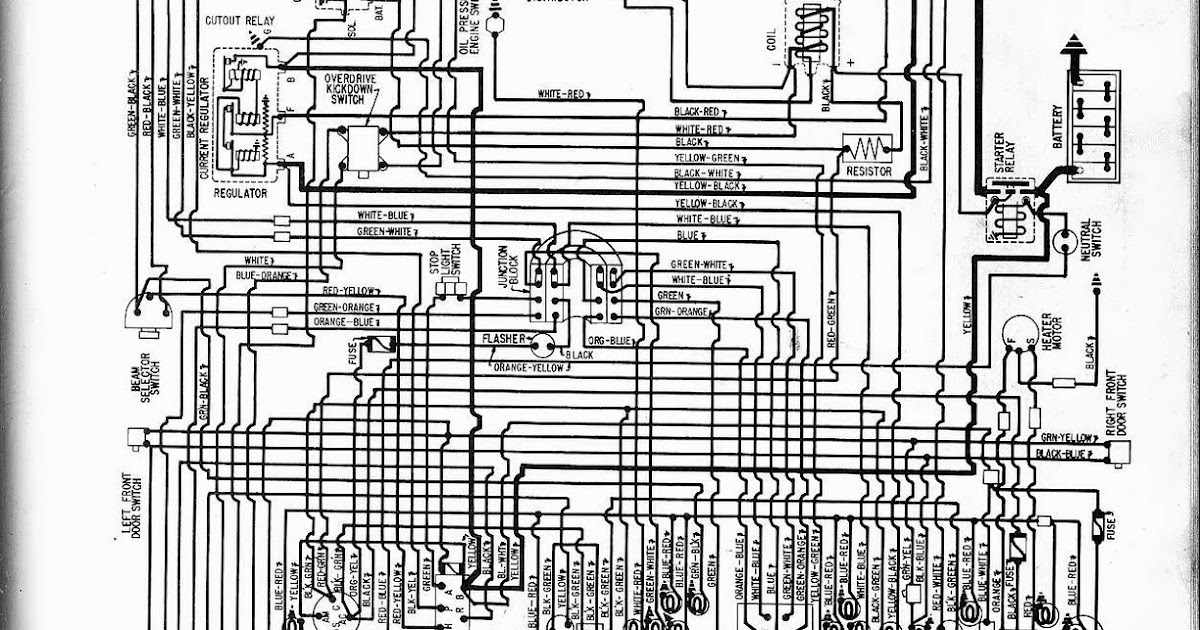
1957 Ford Wiring Diagram – Easy Wiring

1957 Ford Thunderbird Wiring Diagram – Mary Circuit

1957 Ford Fairlane Wiring Diagram
Recently bought a cute 1957 Ford F100, where can I download a wiring
