When it comes to the electrical system of your 1997 Ford Ranger, understanding the wiring diagram for the alternator is crucial. This diagram serves as a roadmap for the electrical connections and can help you troubleshoot any issues that may arise. In this article, we will delve into the importance of the 1997 Ford Ranger Alternator Wiring Diagram and how to effectively use it.
Why are 1997 Ford Ranger Alternator Wiring Diagrams Essential?
The alternator wiring diagram for your 1997 Ford Ranger is essential for several reasons:
- It provides a visual representation of the electrical connections, making it easier to understand how the system works.
- It helps you identify the various components of the alternator system and their respective functions.
- It serves as a reference guide for troubleshooting electrical issues and making repairs.
How to Read and Interpret 1997 Ford Ranger Alternator Wiring Diagrams
Reading and interpreting the alternator wiring diagram for your 1997 Ford Ranger may seem daunting at first, but with a little guidance, it can be a valuable tool:
- Start by familiarizing yourself with the key symbols and color codes used in the diagram.
- Follow the flow of the electrical connections from the alternator to the battery and other components.
- Pay attention to the labels and legends on the diagram to understand the purpose of each wire and connection.
Using 1997 Ford Ranger Alternator Wiring Diagrams for Troubleshooting
When faced with electrical problems in your 1997 Ford Ranger, the alternator wiring diagram can be a lifesaver:
- Use the diagram to trace the source of the issue and identify any faulty connections or components.
- Compare the diagram to the actual wiring in your vehicle to pinpoint any discrepancies.
- Refer to the diagram when making repairs or modifications to ensure the correct installation of new components.
Safety Tips for Working with Electrical Systems
Working with electrical systems, including using wiring diagrams, requires caution and attention to safety:
- Always disconnect the battery before working on any electrical components to prevent the risk of electric shock.
- Avoid working on the electrical system in wet or damp conditions to prevent short circuits.
- Use insulated tools and wear protective gear, such as gloves and safety glasses, when working with electrical components.
1997 Ford Ranger Alternator Wiring Diagram
1997 Ford Ranger Alternator Wiring Diagram – Wiring Diagram Library
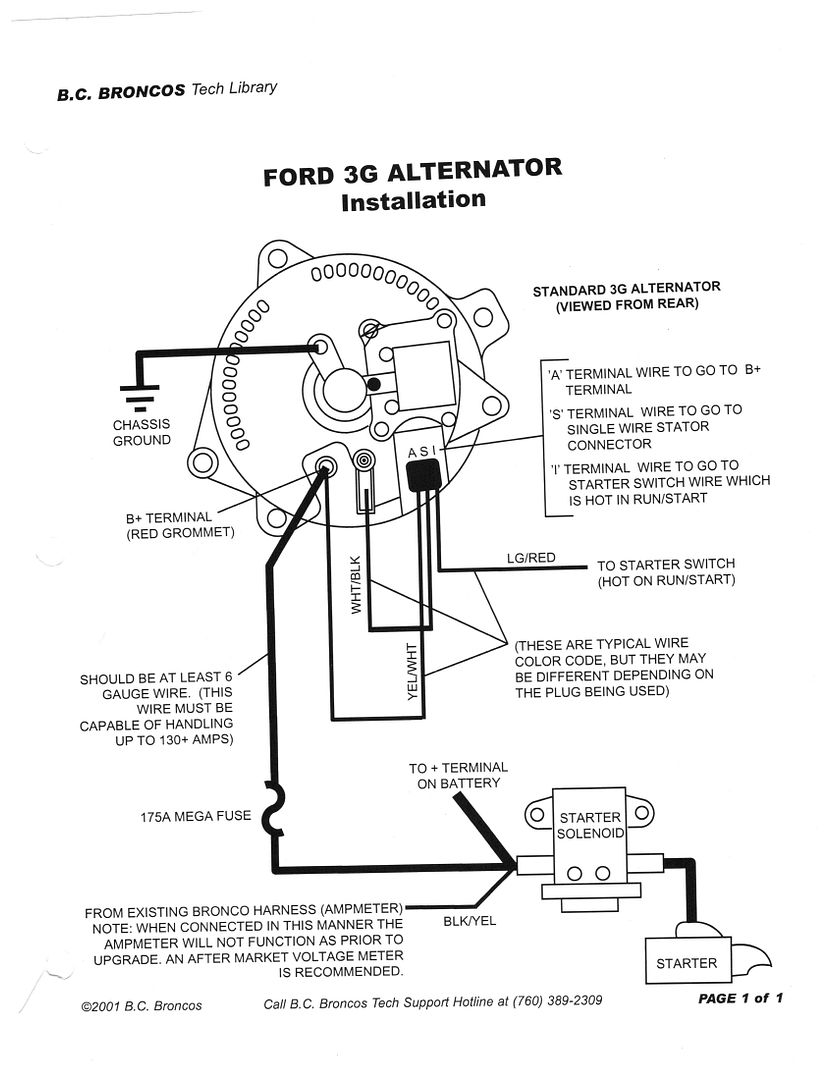
1997 Ford Ranger Alternator Wiring Diagram – Wiring Diagram

®Ford Ranger Alternator Wiring Diagram ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐

1997 Ford Ranger Alternator Wiring Diagram – Wiring Diagram

3 Wire Ford Alternator Wiring Diagram

Ford Ranger Alternator Wiring Diagram Collection – Faceitsalon.com
