When it comes to understanding the electrical system of your 2002 Ford Taurus, having a reliable wiring diagram for the alternator is crucial. The alternator plays a vital role in keeping your vehicle’s battery charged and electrical system running smoothly. In this article, we will delve into the importance of the 2002 Ford Taurus Alternator Wiring Diagram and how it can help you troubleshoot electrical issues effectively.
Why are 2002 Ford Taurus Alternator Wiring Diagrams Essential?
Understanding the wiring diagram for your alternator is essential for several reasons:
- Ensures proper connection of wires for the alternator to function correctly
- Aids in diagnosing electrical issues related to the alternator
- Helps in identifying the correct voltage and current requirements for the alternator
How to Read and Interpret 2002 Ford Taurus Alternator Wiring Diagram
Reading and interpreting a wiring diagram may seem daunting at first, but with the right guidance, it can be a valuable tool. Here are some tips on how to effectively read a 2002 Ford Taurus Alternator Wiring Diagram:
- Understand the symbols and color codes used in the diagram
- Follow the flow of the wiring from the alternator to the battery and other components
- Take note of any fuses or relays that may be involved in the circuit
Using 2002 Ford Taurus Alternator Wiring Diagram for Troubleshooting
When faced with electrical problems in your Ford Taurus, the wiring diagram can be a valuable tool for troubleshooting. Here’s how you can use it effectively:
- Identify the specific wires related to the alternator in the diagram
- Check for continuity and proper voltage levels along the circuit using a multimeter
- Trace back the wiring to locate any potential short circuits or damaged connections
Importance of Safety
Working with electrical systems can be dangerous if proper precautions are not taken. Here are some safety tips to keep in mind when using wiring diagrams for troubleshooting:
- Always disconnect the battery before working on any electrical components
- Use insulated tools to prevent electrical shocks
- Avoid working on electrical systems in wet or damp conditions
2002 Ford Taurus Alternator Wiring Diagram
2002 Ford Taurus Alternator Wiring Diagram – Collection – Wiring

2002 Ford Taurus Alternator Wiring Diagram – Collection – Faceitsalon.com

2002 Ford Taurus Ac Wiring Diagram

2002 Ford Taurus Alternator Wiring Diagram Images – Faceitsalon.com

Wiring An Alternator Diagram
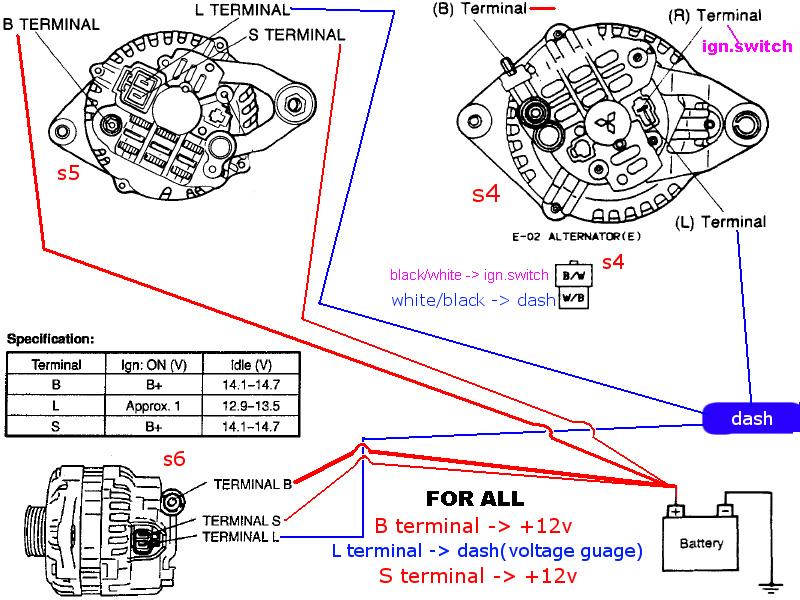
Wiring Diagram Of A Car Alternator
